



Next: The Symmetry Classification of
Up: Molecular Symmetry
Previous: What is Symmetry and
Contents
The classification of objects according to symmetry elements corresponding to operations that
leave at least one common point unchanged gives rise to the point groups.
These are five kinds of symmetry operations and five kinds of symmetry
elements of this kind. These symmetry operations are as follows.
- The identity, E, consists of doing nothing: the corresponding symmetry
element is an entire object. In general, any object undergo this symmetry operation. The
example of the molecule which has only the identity symmetry operation is
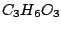 ,
,
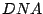 , and
, and 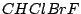 .
.
- The n-fold rotation about an n-fold axis of symmetry,
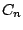 is a
rotation through the angle
is a
rotation through the angle 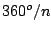 . Particularly, the operation
. Particularly, the operation 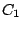 is a rotation
through
is a rotation
through 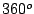 which is equivalent to the identity E.
which is equivalent to the identity E. 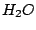 molecule has one twofold
axis,
molecule has one twofold
axis, 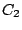 .
. 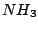 molecule has one threefold axis,
molecule has one threefold axis, 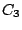 which is associated with two
symmetry operations:
which is associated with two
symmetry operations: 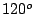 rotation
rotation 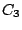 and
and 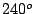 (or
(or 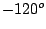 ) rotation
) rotation 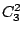 .
. 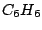 molecule
has one sixfold axis
molecule
has one sixfold axis 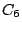 and six twofold axes
and six twofold axes 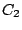 . If a molecule possess several
rotational axes, then the one of them with the greatest value of
. If a molecule possess several
rotational axes, then the one of them with the greatest value of 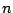 is called the
principal axis. All linear molecules including all diatomics has
is called the
principal axis. All linear molecules including all diatomics has 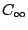 axis
because rotation on any angle remains the molecule the same.
axis
because rotation on any angle remains the molecule the same.
- The reflection in a mirror plane,
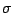 may contain the principal
axis of a molecule, or be perpendicular to it. If the plane contains the principal axis, it
is called vertical and denoted
may contain the principal
axis of a molecule, or be perpendicular to it. If the plane contains the principal axis, it
is called vertical and denoted 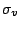 . For instance,
. For instance, 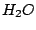 molecule has two
vertical planes of symmetry and
molecule has two
vertical planes of symmetry and 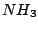 molecule has tree. A vertical mirror plane which
bisects the angle between two
molecule has tree. A vertical mirror plane which
bisects the angle between two 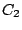 axes is called a dihedral plane and is denoted by
axes is called a dihedral plane and is denoted by
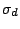 . If the plane of symmetry is perpendicular to the principal axis, it is
called horizontal and denoted
. If the plane of symmetry is perpendicular to the principal axis, it is
called horizontal and denoted 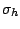 . For instance,
. For instance, 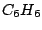 molecule has a
molecule has a
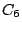 principal axis and a horizontal mirror plane.
principal axis and a horizontal mirror plane.
- The inversion through the center of symmetry is the operation which
transforms all coordinates of the object according to the rule:
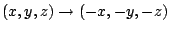 . For instance, a sphere, or a cube has a center of inversion, but
. For instance, a sphere, or a cube has a center of inversion, but  , and
, and
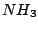 have not.
have not. 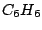 molecule has a center of inversion.
molecule has a center of inversion.
- The n-fold improper rotation about an n-fold axis of symmetry,
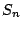 is a combination of two successive transformations. The first transformation is a
rotation through
is a combination of two successive transformations. The first transformation is a
rotation through 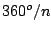 and the second transformation is a reflection through a plane
perpendicular to the axis of the rotation. Note, that neither operation alone needs to be a
symmetry operation. For instance,
and the second transformation is a reflection through a plane
perpendicular to the axis of the rotation. Note, that neither operation alone needs to be a
symmetry operation. For instance, 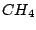 molecule has three
molecule has three 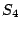 axes.
axes.




Next: The Symmetry Classification of
Up: Molecular Symmetry
Previous: What is Symmetry and
Contents
Markus Hiereth
2005-02-09
Auf diesem Webangebot gilt die Datenschutzerklärung der TU Braunschweig mit Ausnahme der Abschnitte VI, VII und VIII.