



Next: Chirality
Up: Some Consequences of Molecular
Previous: Some Consequences of Molecular
Contents
As we have already discussed a polar molecule is one having a permanent electric dipole
moment. For instance these are 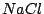 ,
, 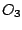 ,
, 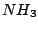 , and many others. It is known that the
rotational absorption transitions can occur only in polar molecules. The group theory give
important instructions, how the molecular symmetry is related to the molecular polarity. For
instance, if a molecule belongs to the group
, and many others. It is known that the
rotational absorption transitions can occur only in polar molecules. The group theory give
important instructions, how the molecular symmetry is related to the molecular polarity. For
instance, if a molecule belongs to the group 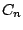 , where
, where 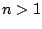 , then it cannot have a component
of the dipole moment perpendicular to the symmetry axis, because a dipole moment which exist in
one direction perpendicular to the axis is cancelled by an opposing dipole. A dipole moment in
these molecules can be only parallel to the molecular axis. The same is valid for any
of the
, then it cannot have a component
of the dipole moment perpendicular to the symmetry axis, because a dipole moment which exist in
one direction perpendicular to the axis is cancelled by an opposing dipole. A dipole moment in
these molecules can be only parallel to the molecular axis. The same is valid for any
of the 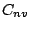 group molecule. The molecules which belongs to all other groups, but
group molecule. The molecules which belongs to all other groups, but 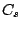 ,
cannot have a permanent dipole moment, because they always have symmetry operations transforming
one end of the molecule into another. Thus, only the molecules which belong to the
,
cannot have a permanent dipole moment, because they always have symmetry operations transforming
one end of the molecule into another. Thus, only the molecules which belong to the
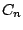 ,
, 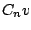 , or
, or 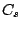 group can have a permanent dipole moment.
group can have a permanent dipole moment.




Next: Chirality
Up: Some Consequences of Molecular
Previous: Some Consequences of Molecular
Contents
Markus Hiereth
2005-02-09
Auf diesem Webangebot gilt die Datenschutzerklärung der TU Braunschweig mit Ausnahme der Abschnitte VI, VII und VIII.