The Newtonian kinematic equations describe the motion of a point mass along a well-defined path that is defined by its initial conditions such as its acceleration and velocity. The energy of a particle moving in a potential V(x) and with an impulse of p = mv (m: mass, v: velocity) is given by E = Ekin + V(x). Since Ekin = ½mv² and p = mv and therefore Ekin = p²/2m and altogether one can finally obtain the total energy equation:
E = p²/2m + V(x)
Since energy is conserved quantity, i.e. energy is time independent and impulse is given by p = m · dx/dt one can easily obtain the ordinary differential equation (ODE) relative to x. The solution (or particle motion)can be obtained at any point in time if x(t = 0) and p(t = 0) are known.
Example:
Harmonic oscillator; V(x) = ½ kx², E =
p²/2m + ½ kx² Þ E = ½ m (dx/dt)² + ½ kx²
Having constant energy one can easily plot figures E = p²/2m + ½ kx² in (x,p)-phase space for different
energies E1, E2,..: 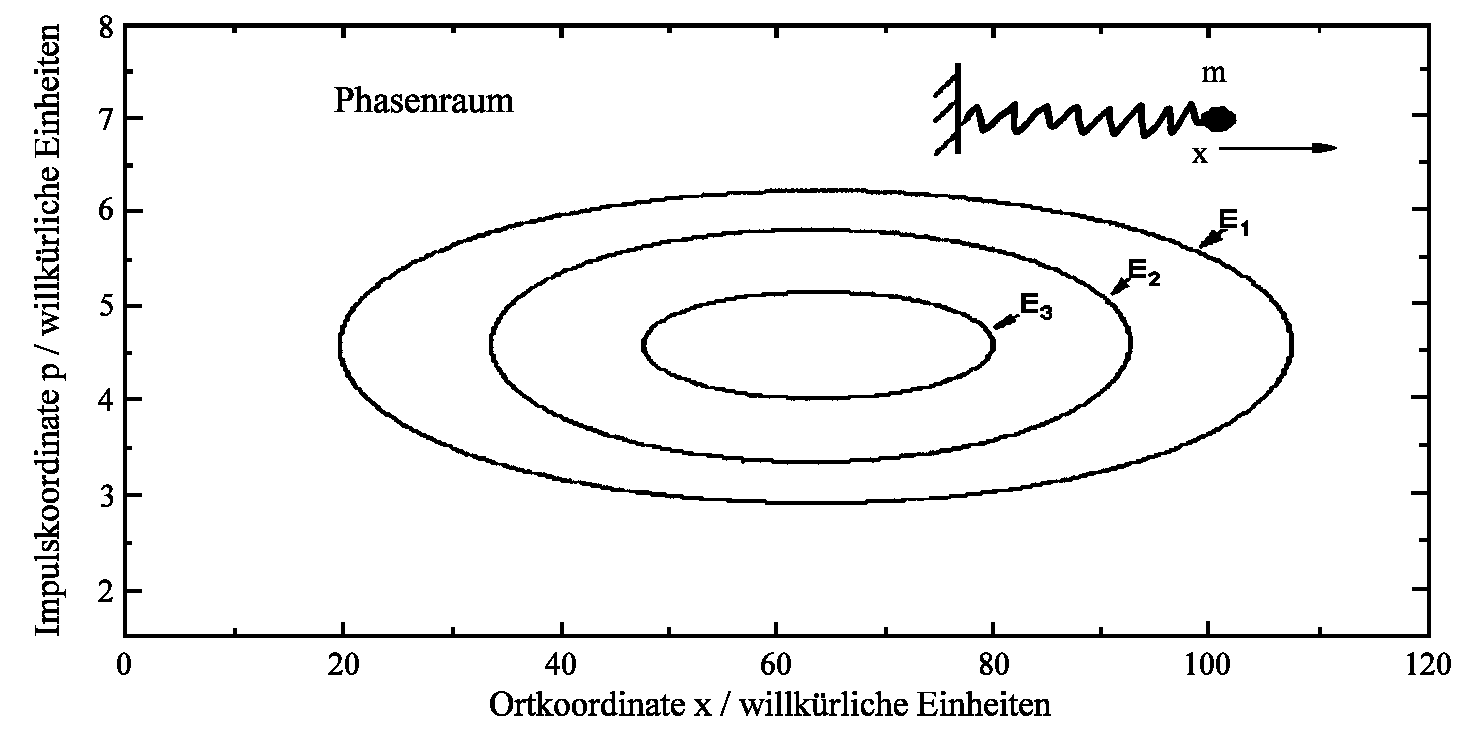
The elegance in point mass movement (classical) description is observable when using the Hamilton
function (H).
All equations of motion in classical mechanics are
continuous functions.
In the case of gravitational interactions, classical physics is especially useful and gives very good descriptions of the motions of planets, moons and artificial satellites. All information about the orbits of these objects in space can be calculated using classical mechanics. Its application is limited in only a few cases: for instance, Mercury perihelion rotation can be predicted with the accuracy of "only" 99,2%; the remainder requires improved theory - the General Relativity Theory. It's one of two biggest theories in the world. The important features of another big theory, "Quantum Mechanics", (Why quantum mechanics?) will be discussed a bit later in this semester. Unification of the two theories is a great aspiration of mankind.
Another theory that brilliantly describes Maxwell equations is called
electromagnetic theory. The Maxwell equations describe light as an electromagnetic
wave. If we were to move towards the Sun we would increasingly feel affected by the heat inherent in the electromagnetic radiation produced by the Sun.
The first discontinuous functions can be seen in spectroscopy:
1814 Fraunhofer studied lines in the sun's electromagnetic spectrum 
1860 Bunsen and Kirchhoff developed spectral
analysis
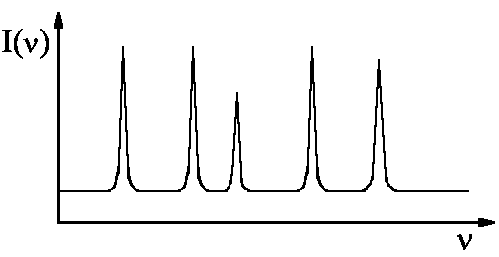 |
| The line spectrum is characteristic of the atoms that are contained in the sample characteristic |
1885 Balmer developed the empirical formula for the positions of lines emitted by hydrogen atoms that follows:
ν = RH(1/4−1/m²) m = 3, 4, 5......
RH: Rydberg constant = 3,29 · 1013 Hz
These measurements do not agree with the classical theory. Nevertheless, scientists were not initially concerned with these phenomena. At the time, their interests were focused on the theoretical Black Body Radiator.
![]()
Auf diesem Webangebot gilt die Datenschutzerklärung der TU Braunschweig mit Ausnahme der Abschnitte VI, VII und VIII.