



Next: Rotational Structure of Electronic
Up: Electronic Transitions
Previous: Electronic Transitions
Contents
Selection Rules for Electronic Transitions
in Diatomic Molecules
The selection rules
for optical transitions between different electronic states of a diatomic molecule are shown in
Table 4.
Table 4:
Selection Rules for Electronic Transitions in Diatomic Molecules
| Allowed Transitions |
Examples |
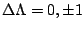 |
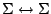 , ,
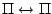 , ,
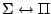 , ,
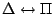 |
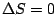 |
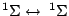 , ,
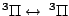 , ,
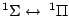 , ,
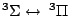 |
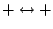 |
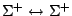 |
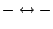 |
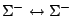 |
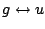 |
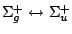 , ,
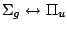 |
If we consider the rotational states as well, it is required that the total angular momentum of
photon and molecule remains constant. In general, the selection rules for the total angular
momentum 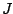 are as follows:
are as follows:
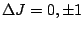 however, for
however, for
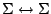 transitions the
transitions the 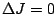 transition is forbidden. These rules are summarized in
table 5 below.
transition is forbidden. These rules are summarized in
table 5 below.
Table 5:
Selection Rules for rotational quantum number 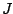 in Electronic Transitions
in Electronic Transitions
| Electron Transition |
Allowed transitions |
Name |
 |
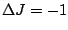 |
P branch |
| |
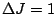 |
R branch |
| |
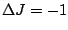 |
P branch |
| all others |
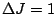 |
R branch |
| |
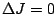 |
Q branch |




Next: Rotational Structure of Electronic
Up: Electronic Transitions
Previous: Electronic Transitions
Contents
Markus Hiereth
2005-01-20
Auf diesem Webangebot gilt die Datenschutzerklärung der TU Braunschweig mit Ausnahme der Abschnitte VI, VII und VIII.
![]() are as follows:
are as follows:
![]() however, for
however, for
![]() transitions the
transitions the ![]() transition is forbidden. These rules are summarized in
table 5 below.
transition is forbidden. These rules are summarized in
table 5 below.